3D Asset Workflow: Collisions
- ◇ Main Steps
- 3D Asset Workflow: Concepting
- 3D Asset Workflow: Sculpting
- 3D Asset Workflow: Retopology
- 3D Asset Workflow: UV Mapping
- 3D Asset Workflow: Baking
- 3D Asset Workflow: Texturing
- 3D Asset Workflow: Asset Assembling
- 3D Asset Workflow: Naming the Asset
- 3D Asset Workflow: LODs
- 3D Asset Workflow: Exporting to Editor
- 3D Asset Workflow: Completed asset checklist
- ◇ Additional Steps
- 3D Asset Workflow: Alternative Textures
- 3D Asset Workflow: Billboards
- 3D Asset Workflow: Blocksets
- 3D Asset Workflow: Collisions
- 3D Asset Workflow: Sikailu
- 3D Asset Workflow: Sway
- 3D Asset Workflow: Tile Textures and Trimsheets
- 3D Asset Workflow: Tintmask
- 3D Asset Workflow: Vegetation
- ◇ General Tips and Troubleshooting
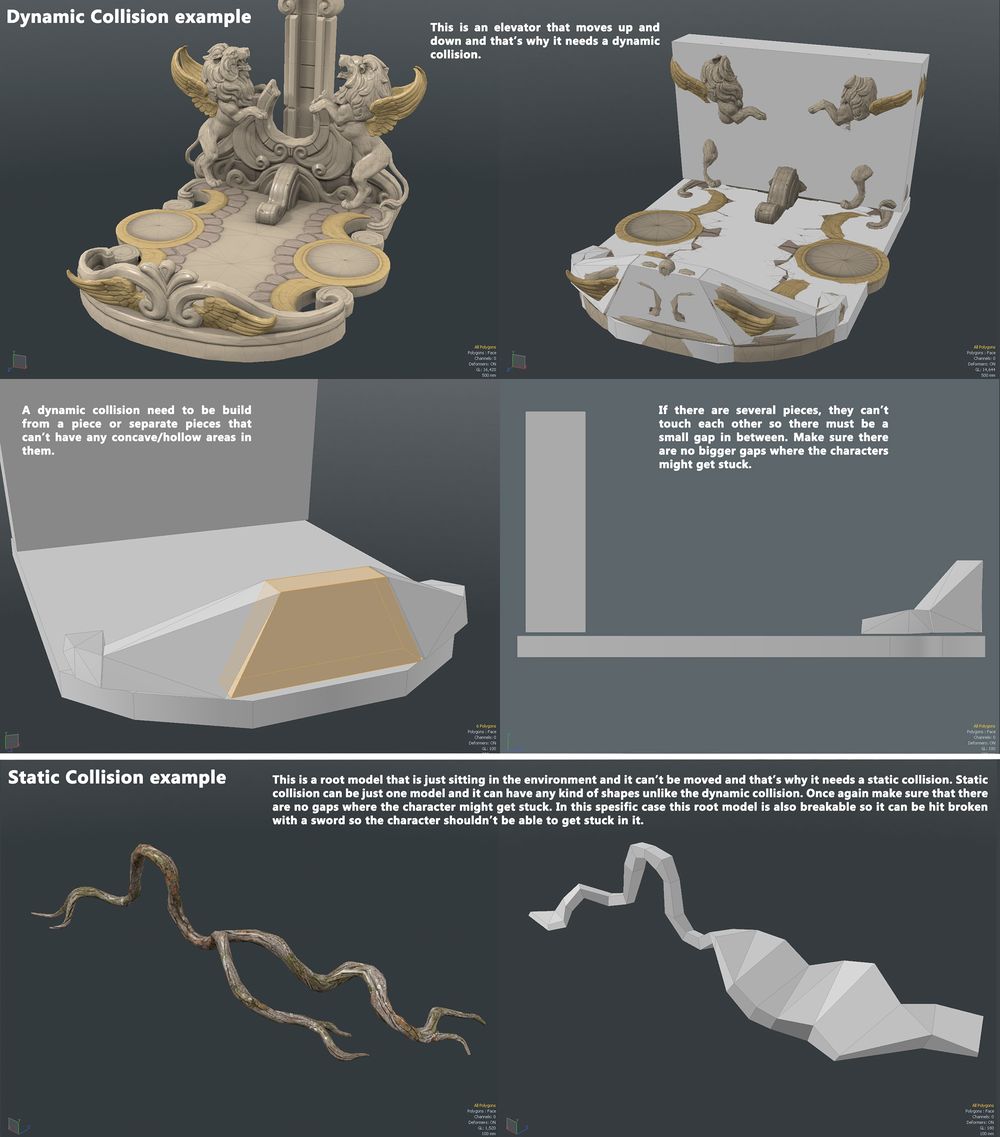
Collisions
- Collisions are very simple and very low poly meshes that tell the game engine where the collideable edges of the model are
- Collisions can be divided into two categories; static and dynamic
- Static objects are stationary, dynamic objects are dynamic, and can be e.g. thrown or kicked around the level, or otherwise interacted with
- When making collisions, be wary of sharp edges or holes, in which the characters can get stuck
Static Collisions
- Collisions for objects which can't be manipulated by the characters in the game
- For example just a static piece of environment in the game that doesn't move in any way
- Can be made in one layer with multiple objects colliding with each other
- The collision layer must be parented with the original object
Naming: xx_static_collision
Example of the hierarchy:
- box
- box_static_collision
Dynamic Collisions
- Collisions for objects which move and/or can be manipulated by the characters in the game, for example dropped or kicked
- The collision objects can't be concave, so in most cases the dynamic collision must be made with many objects
- These must be separated to different layers, and can't collide with each other
- All the dynamic collision layers must be parented with the original object
Naming: xx_collision_dynamic(_01)
Example of the hierarchy:
- box
- box_collision_dynamic_01
- box_collision_dynamic_02
- box_collision_dynamic_03
Adding Collisions in Editor
- Once the collisions for each object are done in Modo, and the models are exported to the Editor, you need to add Components to the type to make the collisions actually work
- Most of the time you can just copy and paste the needed components from some existing model, that is similar to your new model
- It's good to copy the Components from objects that have similar material or size, but the shape doesn't matter because your object will use the collision model you made for it in Modo
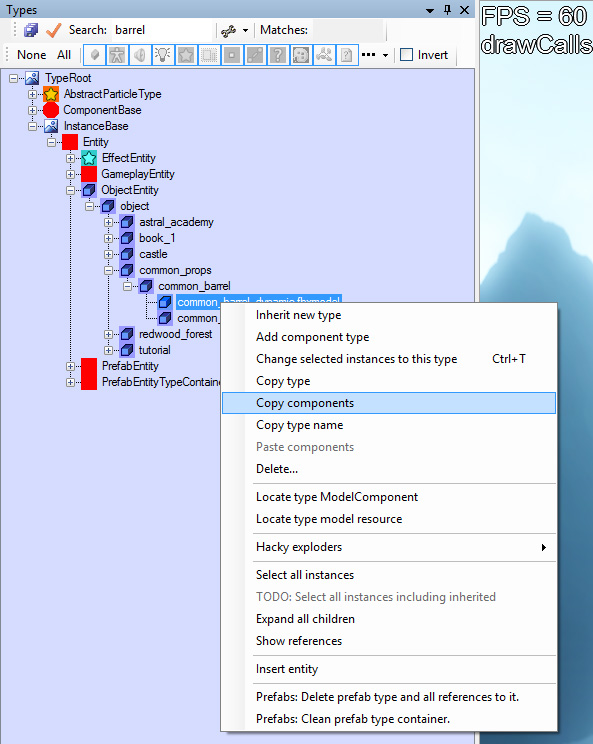
Image Guide to Adding Collisions in Editor, with Explanatory Texts
- Select the model in Type Tree and see its Properties
- There should already be these Model Components
- ModelComponent
- TransformComponent
- You need to either copy or search and add these components
- HittableComponent
- ContactEffectCreatorComponent
- PhysicsComponent
- StaticMesh (for static collision)
- ConvexCompound (for dynamic collision)
- Copy by selecting the object you want to copy from in Type Tree and right click "Copy Components", don't copy ModelComponent and TransformComponent, DO NOT COPY FROM DYNAMIC TO STATIC OBJECT OR FROM STATIC TO DYNAMIC!
- If there aren't similar objects with collision in the game, Add by selecting the object you want to add to in Type Tree and right click "Add Component Type", then search the needed components
- In this case, you can either Add or Add and Inherit. By just Adding, the Components stay shared with the type you copied it from, with Add and Inherit you create a separate copy of the Component